BME prizes at physics students' conference
2021. May 17.
BME physics students win three first prizes, two second prizes, and a third prize, at this year's National Scientific Students' Associations Conference. Results in pdf, in Hungarian.


2021. May 17.
BME physics students win three first prizes, two second prizes, and a third prize, at this year's National Scientific Students' Associations Conference. Results in pdf, in Hungarian.

2021. May 13.
New Vorbuchner helium liquifier, recycling helium for several research and educational laboratories within and outside BME, have been installed succesfully in building L.
Images at the Department of Physics.
Detailed description of the project in Hungarian.

2021. May 05.
New results from the Self-organization and Self-assembly Research Group, on the self-organization of nanoparticles and molecules, is published in Science Advances.
Group website: https://dept.physics.bme.hu/Self-organization
A. J. Ackroyd, G. Holló, H. Mundoor, H. Zhang, O. Gang, I. I. Smalyukh, I. Lagzi, E. Kumacheva
Self-organization of nanoparticles and molecules in periodic Liesegang-type structures
Science Advances 7, eabe3801, DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abe3801
2021. April 18.
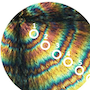
Our colleagues' new results may enable the creation and experimental investigation of topologically protected quantum states. Published in Nature Communications.
Philip Beck, Lucas Schneider, Levente Rózsa, Krisztián Palotás, András Lászlóffy, László Szunyogh, Jens Wiebe & Roland Wiesendanger
Spin-orbit coupling induced splitting of Yu-Shiba-Rusinov states in antiferromagnetic dimers
Nature Communications volume 12, Article number: 2040 (2021)
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-22261-6

2021. February 10.
Will quantum technology impact computer networks? An online seminar series organized by Nokia Bell Labs and the BME Insitute of Physics, starting on Feb 18.
Webpage of the event: https://physics.bme.hu/dqs2021?language=en
2021. January 24.
Must-see physics experiments - online physics lecture for high-school students and their teachers, via the YouTube channel of Károly Härtlein, on Jan 22, 16:00.
Must-see Physics Experiments

2021. January 08.
Study on the natural geometry of fragmentation, by our colleague János Török and his coauthors, is selected by Science as one of their 10 favorite science news stories in 2020.

2021. January 06.
We mourn the tragic loss of our colleague Dr. János Pipek, honorary professor of our Institute, former Dean and Vice Dean of Education of the BME Faculty of Sciences.

2020. December 15.
The device, thinner than a hair, can sense tiny changes of magnetic fields. Experimental work published in Nano Letters by BME's Péter Makk and co-authors at Uni Basel.
2020. December 03.
