Electrically controlled optical diode mechanism in a magnetoelectric crystal was discovered by the BME Complex Magnetic Structures research group. Published in Physical Review Letters.
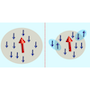
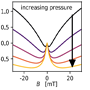
The research group, leading an international collaboration, has studied the optical properties of a magnetoelectric antiferromagnet (Ba2CoGe2O7) in the terahertz frequency range. They found a optical diode effect, also known as non-reciprocal light absorption, meaning that a crystal absorbs the electromagnetic radiation for a given propagation direction but transmits most of the light for the counterpropagating radiation. The BME researchers could control the optical diode effect by electric fields. This study also revealed that tuning the electric field can switch the state of the antiferromagnetic domains of the sample, and this is the mechanism that allows for an electrical control of the optical diode effect. These results might enable the design of light switches in the terahertz domain based on antiferromagnets similar to Ba2CoGe2O7.
J. Vít, J. Viirok, L. Peedu, T. Rõõm, U. Nagel, V. Kocsis, Y. Tokunaga, Y. Taguchi, Y. Tokura, I. Kézsmárki, P. Balla, K. Penc, J. Romhányi, and S. Bordács
In Situ Electric-Field Control of THz Nonreciprocal Directional Dichroism in the Multiferroic Ba2CoGe2O7
Phys. Rev. Lett. 127, 157201 (2021)