2023. szeptember 27.
Theoretical physicists of BME Institute of Physics published new numerical results on the efficiency of the surface code error correction protocol in the journal Quantum.
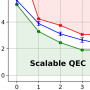
To perform long computations, the quantum information that quantum computers work on has to be protected against environmental noise. This requires quantum error correction (QEC), whereby each logical qubit is encoded into collective quantum states of many physical qubits. We studied, using numerical simulation, how well the most promising quantum error correcting code, the so-called Surface Code can protect quantum information against a combination of so-called coherent errors (a type of calibration errors) and readout errors. We found that the Surface Code provides better protection as the code is scaled up, as long as the error levels are below a threshold. This threshold is close to the well-known threshold of another combination of errors: incoherent errors (a type of error arising from entanglement with a quantum environment) and readout errors. We also found (as shown in the accompanying image) that the Surface Code is more robust against readout errors than coherent errors. Note that we used the so-called phenomenological error model: we modeled the noise channels very precisely, but did not do a modeling of the code on the quantum circuit level.
Coherent errors and readout errors in the surface code
Áron Márton and János K. Asbóth